Economic Evolution and Milestones
The economic landscape of Japan from 1960 to 1990 is marked by significant transitions and pivotal events that shaped its trajectory. In the 1960s, Japan experienced an era of high growth characterized by rapid industrialization and technological advancements, propelling it to become a leading global economic powerhouse. This period saw Japan leveraging its industrial policies and economic strategies to boost production and exports, fostering unprecedented economic expansion.
The 1970s brought challenges such as the oil crises, which necessitated strategic economic adjustments. Japan adeptly navigated these challenges through policy reforms and a shift towards more energy-efficient technologies. This period also saw the emergence of significant government involvement in steering economic recovery and maintaining growth momentum.
The 1980s marked a transformative era with technological advancements and market reforms, further enhancing Japan's economic position. However, the decade ended with the bubble economy, characterized by excessive speculation and inflated asset prices, which ultimately led to significant economic repercussions.
Reflecting on these decades, several lessons emerge about the resilience and adaptability of Japan's economy in response to both opportunities and crises. These insights are crucial for understanding how Japan navigated its post-war economic challenges and positioned itself for future growth, despite the setbacks faced during the bubble economy.
This report has been prepared using content written in english from medical articles, academic papers, clinical trials, patents and IP, legal and court filings, popular web sites, credible web sites, global and niche news sources and wiki. Content and language choices can be finely focused by users with access to corpora.ai advanced features.
1. The Era of High Growth (1960s)
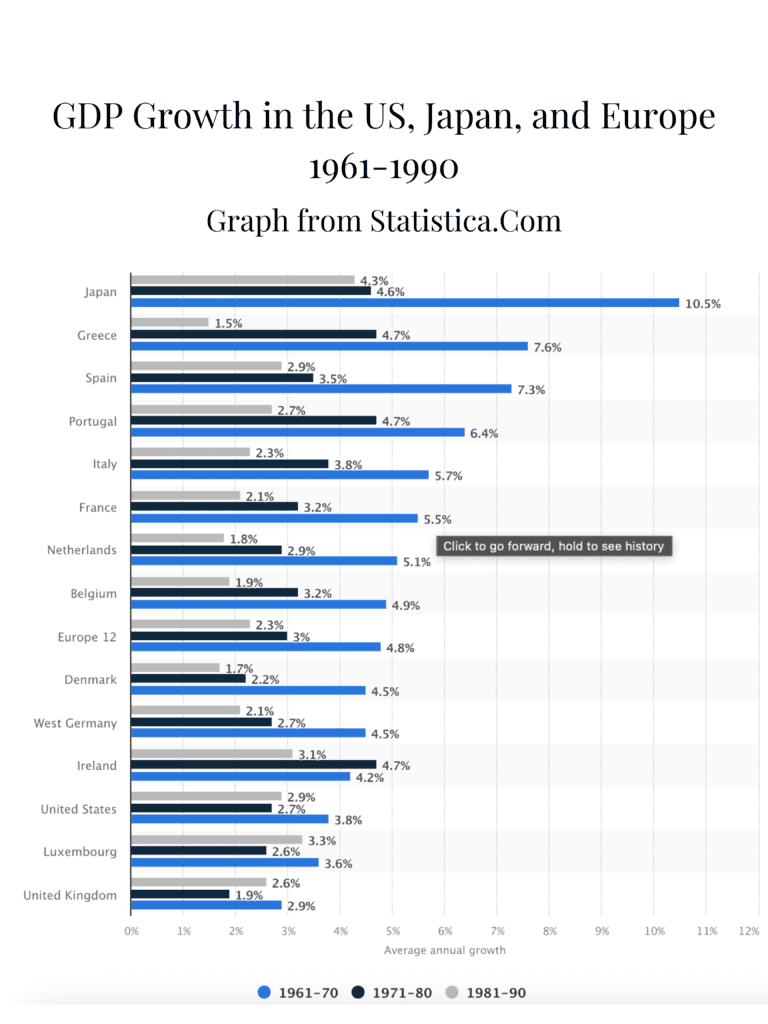
The 1960s marked a transformative era for the Japanese economy, characterized by exceptional growth rates. During this period, Japan achieved growth rates similar to China's economic boom in later decades, frequently exceeding 10 percent annually[1]. This growth was primarily driven by rapid industrialization and expansion in sectors such as steel, chemicals, heavy electric equipment, and shipbuilding[4]. By the 1970s, Japan emerged as the world's second-largest capitalist economy, largely due to its impressive economic performance in the previous decade[6]. The era was marked by significant productivity improvements, with the productivity gap halving by 1970 compared to 1960, and further decreasing by 1990[3]. The economic strategy of Japan during this time involved meticulous government interventions that aimed to balance trade and foreign investment while stimulating domestic industries[4]. Japan's economic achievements during this period were so pronounced that extrapolations suggested it might have overtaken the U.S. economy by the 1980s, had the growth continued at the same pace[2]. The country's industrial policies in the 1950s and 1960s were also crucial in fostering the rapid development of its domestic market, reducing dependence on imports, and achieving a high degree of self-reliance[5]. The economic policies encouraged high levels of private savings and investments, channeling about 30 to 35 percent of Japan's national output into investments[7]. This focus on investment, coupled with technological advancements and government policies, positioned Japan as a leading economic power by the end of the 1960s[8].
2. Oil Crises and Economic Adjustments (1970s)
During the 1970s, Japan's economic landscape was significantly influenced by the global oil crises. The 1973 oil crisis marked a turning point, leading to a noticeable slowdown in Japan's rapid economic growth, which had been robust since the post-war era [13]. This slowdown affected various sectors, including the automotive industry, which adapted by focusing on fuel-efficient and reliable vehicles to maintain international competitiveness. Companies like Mitsubishi used this as an opportunity to expand abroad [10]. Furthermore, the crisis prompted significant adjustments in Japan's economic policies and practices. For instance, the appreciation and subsequent depreciation of the yen during this period reflected the economic volatility caused by the oil crisis [13]. The crisis also highlighted Japan's heavy reliance on oil imports, emphasizing the need for a more self-reliant energy strategy [11]. As a result, Japan initiated measures to diversify its energy sources and enhance energy security [12]. The economic adjustments during this period also led to a shift in Japan's industrial focus. By the late 1970s, the country began transitioning from heavy manufacturing to a more service-oriented economy [14]. Additionally, the Japanese government implemented a "petroleum and coal tax" to tackle energy security issues post-crisis [10]. This era of economic adjustment was also marked by increased competition in domestic markets, such as the media sector, where new players emerged, challenging established companies [9]. Overall, the oil crises of the 1970s forced Japan to reevaluate and adjust its economic strategies, leading to both challenges and new growth opportunities.
3. Technological Advancements and Market Reforms (1980s)
In the 1980s, Japan experienced significant technological advancements and market reforms, contributing to its economic growth and global influence. The Japanese companies' expansion overseas intensified during this period, supported by a strong domestic economy [15]. The era also saw a surge in technological innovations, such as the development of the GY6 engine by Honda for motor scooters [18], and breakthroughs in Kawai-type multianvil (KMA) ultrahigh-pressure technology by Japanese scientists, which provided critical insights into earth sciences [16]. Japanese consumer electronics and automotive industries also flourished, leading to a formidable trade surplus and wealth [20]. Notably, Japanese companies captured significant global market shares in semiconductors, accounting for about 51% of the global semiconductor market by the end of the 1980s [17]. Furthermore, the decade witnessed a boom in real estate and equity markets, creating a speculative bubble that later burst, initiating a prolonged economic stagnation known as the "Lost Decade" [19]. Despite these challenges, Japan managed to leverage its technological advancements, becoming a leading economic power in Asia and globally [21].
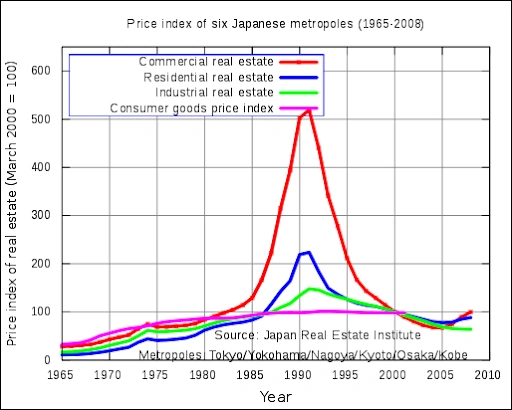
4. The Bubble Economy and Its Consequences (Late 1980s)
The late 1980s marked the zenith of Japan's economic bubble, characterized by rampant asset price inflation driven by excessive speculation and lenient monetary policies by the Bank of Japan [25]. This period saw the Nikkei 225 index reaching unprecedented heights, fueled by speculative investments in both real estate and equities, with stock prices soaring to price-to-earnings multiples in the 50s and beyond [24][26]. As investors sought high returns, asset prices escalated, notably in the real estate sector, where land values tripled in urban areas by the end of 1990 [28]. Japanese consumers also played a significant role during this bubble period, transitioning into extravagant spenders [22]. This economic exuberance culminated in a profound crash when the Bank of Japan implemented monetary tightening to curb speculation, leading to a collapse in asset prices by 1991 [25]. The bursting of this bubble resulted in a prolonged economic stagnation, often referred to as Japan's "Lost Decade," as the country struggled to recover from the aftermath of the asset price deflation [30][31]. Many Japanese industries, such as real estate and stock markets, faced severe setbacks, with the Nikkei 225 taking decades to approach its pre-crash highs [26][29]. The cultural impact of this economic era was also evident, as symbols like Japanese baseball stadiums faced closures due to financial pressures [23]. The late 1980s bubble economy in Japan serves as a cautionary tale of how unchecked speculative fervor and inadequate regulatory responses can lead to significant economic downturns [27].
5. Long-term Economic Impacts and Lessons Learned
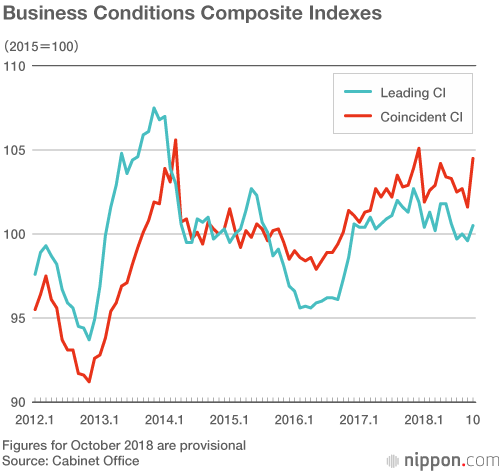
The long-term economic impacts and lessons learned from Japan's economic evolution between 1960 and 1990 are multifaceted. Natural disasters, such as the 1995 Kobe earthquake, had varied perceptions regarding their long-term impact on the economy. Some studies suggest that the damage from the Kobe earthquake did not have a significant long-term impact on Japan's overall economy or the city itself [34][37]. In contrast, the devastation from the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011 has been analyzed for both its immediate and long-term impacts on the Japanese economy, with some suggesting that the fears of significant long-term economic disruption may have been overestimated [35][36]. The persistent low-interest rates maintained by the Bank of Japan also present long-term challenges for economic growth and have sparked concerns from economic policymakers [32]. These financial policies, along with demographic issues like a matured manufacturing sector and an aging population, have contributed to a long-term recession in Japan, beginning in the 1990s and extending for decades [39]. Moreover, shifts in trade policies, particularly in the automotive sector, could exacerbate economic challenges if domestic production moves abroad, impacting economic outputs and employment [33]. Despite these challenges, the size and global influence of Japan's economy mean that even moderate economic changes can have significant worldwide consequences [38].